 |
Austin TX (SPX) Mar 31, 2011 Astronomers led by graduate student Emmanouil "Manos" Chatzopoulos and Dr. J. Craig Wheeler of The University of Texas at Austin have found another extremely bright, rare supernova to add to the new class of exploding stars that University of Texas astronomers identified a few years ago. Supernova 2008am is one of the most intrinsically bright exploding stars ever observed. The team's research reveals that this supernova is the brightest "self-interacting" supernova yet discovered. In this type of stellar explosion, the extreme brightness is caused by interaction between the explosion shockwave and a shell of material previously expelled from the star. This research is published in the current issue of The Astrophysical Journal. Supernova 2008am is 3.7 billion light-years away. At its peak luminosity, it was over 100 billion times brighter than the Sun. It emitted enough energy in one second to satisfy the power needs of the United States for one million times longer than the universe has existed. In-depth studies of this supernova are helping the team to understand the science behind this new class of exploding stars. The supernova was discovered by the ROTSE Supernova Verification Project (RSVP, formerly called the Texas Supernova Search), which uses the 18-inch robotic ROTSE IIIb Telescope at The University of Texas at Austin's McDonald Observatory. It was followed up by astronomers using some of the world's largest ground-based telescopes, as well as telescopes in space, in a variety of wavelengths. These include the Hobby-Eberly Telescope, the Keck Telescope, PAIRITEL, the Very Large Array, and the Swift satellite. Chatzopoulos' detailed analysis of the light from SN 2008am revealed that is not a pair-instability supernova, the explosion of a massive star the light from which is powered by radioactive decay. Rather, this supernova's extraordinary luminosity most likely comes from interaction between the debris from the star's explosion running into an envelope of gas around the star that the star had previously ejected. This model is called "circumstellar interaction." The researchers suspect that the progenitor star for this supernova might have been of the type known as a "luminous blue variable." These massive stars puff off layers of material in episodes. The most famous example is Eta Carinae. Prior to this discovery, the Texas Supernova Search's found the first two "brightest supernovae ever" in SN 2005ap and 2006gy. The group has found five of the dozen published examples of this new class of stars, which it has dubbed "super-luminous supernovae," or SLSNe. SLSNe are about 100 times brighter than standard core-collapse supernovae, but extremely rare. Normal supernovae go off at a rate of about one per century in a galaxy; SLSNe may be more than a thousand times more rare. "We're now in the process of converting our discoveries into real science rather than just a new thing," Wheeler said. "That makes it a little bit less flashy, but of course that's where the science really is, digging deeply into the nature of these very bright events. This new supernova has given us important new clues to their behavior." Studies of SLSNe have led to new insights, Chatzopoulos said. "For the first time, we're probing high-mass stellar death. The traditional ideas we have about how supernovae are powered, why they are so bright, do not seem to apply for the case of these super-luminous supernovae. There are other mechanisms involved." Not all SLSNe are the same. "There's a variety of progenitor stars that can give different outcomes," Chatzopoulos said. "It's a zoo." The common factor is their luminosity. The fate of different stars depends on their mass, Wheeler said. He defines three categories of high-mass stars that explode as supernovae: In the least massive case, around 10 to 20 solar masses, a star collapses in on itself because its iron core cannot hold out against the crushing gravity of the star's weight. This is the classic "core-collapse supernova" with normal brightness. The second progenitor category consists of more massive stars, perhaps up to 100 solar masses. This type of star puffs off layers of material before it dies. The interaction between the supernova ejecta and the previously puffed-off material can cause the supernova to brighten to the superluminous range. The final category includes the most massive progenitor stars, those more than 100 solar masses. In this case, "the current state of the art predicts that they make matter and anti-matter, electronpositron pairs, because they are so hot," Wheeler said. "That process destabilizes the whole star and it contracts, ignites the thermonuclear fuel, and then explodes, blowing the whole star up." These are called "pair-instability" supernovae. Of the three types of explosions Wheeler describes, the first two would leave behind a stellar remnant in the form of a neutron star or black hole. The third and most massive, though, would explode completely, leaving no remnant. Though they set a record, the team isn't finished studying super-luminous supernovae. Their work on understanding SN 2008am might explain the origins of half of the known examples, but as Wheeler said, "to a scientist, the interesting thing is, what's the other half? ... We want to understand them all before we're done."
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links University of Texas at Austin Astronomy News from Skynightly.com
 Suzaku Shows Clearest Picture Yet Of Perseus Galaxy Cluster
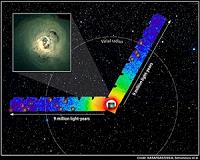
Suzaku Shows Clearest Picture Yet Of Perseus Galaxy ClusterGreenbelt MD (SPX) Mar 25, 2011 X-ray observations made by the Suzaku observatory provide the clearest picture to date of the size, mass and chemical content of a nearby cluster of galaxies. The study also provides the first direct evidence that million-degree gas clouds are tightly gathered in the cluster's outskirts. Suzaku is sponsored by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) with contributions from NASA and p ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |