 |
Syracuse, NY (SPX) Mar 29, 2011 Shortly after experiments on the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at the CERN laboratory near Geneva, Switzerland began yielding scientific data last fall, a group of scientists led by a Syracuse University physicist became the first to observe the decays of a rare particle that was present right after the Big Bang. By studying this particle, scientists hope to solve the mystery of why the universe evolved with more matter than antimatter. Led by Sheldon Stone, a physicist in SU's College of Arts and Sciences, the scientists observed the decay of a special type of B meson, which are created when protons traveling at nearly the speed of light smash into each other. The work is part of two studies published in the March 28 issue of Physics Letters B. Stone leads SU's high-energy physics group, which is part of a larger group of scientists (the LHCb collaboration) that run an experiment at CERN. The National Science Foundation (NSF) funds Stone's research group. "It is impressive to see such a forefront physics result produced so soon after data-taking commenced at the LHC," said Moishe Pripstein, program director for the NSF's Elementary Particle Physics program. "These results are a tribute both to the ingenuity of the international collaboration of scientists and the discovery potential of the LHC." Scientists are eager to study these special B mesons because of their potential for yielding information about the relationship between matter and antimatter moments after the Big Bang, as well as yet-to-be described forces that resulted in the rise of matter over antimatter. "We know when the universe formed from the Big Bang, it had just as much matter as antimatter," Stone says. "But we live in a world predominantly made of matter, therefore, there had to be differences in the decaying of both matter and antimatter in order to end up with a surplus of matter." All matter is composed of atoms, which are composed of protons (positive charge), electrons (negative charge) and neutrons (neutral). The protons and neutrons are composed, in turn, of even smaller particles called quarks. Antimatter is composed of antiprotons, positrons (the opposite of electrons), antineutrons, and thus anti-quarks. While antimatter generally refers to sub-atomic particles, it can also include larger elements, such as hydrogen or helium. It is generally believed that the same rules of physics should apply to both matter and antimatter and that both should occur in equal amounts in the universe. That they don't play by the same rules or occur in equal amounts are among the greatest unsolved problems in physics today. B mesons are a rare and special subgroup of mesons composed of a quark and anti-quark. While B mesons were common after the Big Bang, they are not believed to occur in nature today and can only be created and observed under experimental conditions in the LHC or other high-energy colliders. Because these particles don't play by the same rules of physics as most other matter, scientists believe B mesons may have played an important role in the rise of matter over antimatter. The particles may also provide clues about the nature of the forces that led to this lack of symmetry in the universe. "We want to figure out the nature of the forces that influence the decay of these [B meson] particles," Stone says. "These forces exist, but we just don't know what they are. It could help explain why antimatter decays differently than matter." In 2009, SU's experimental high-energy physics group received more than $3.5 million from the NSF through the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) for its research as part of the LHCb collaboration at CERN. The LHCb, one of four large particle detectors located in the LHC ring, is dedicated to searching for new types of fundamental forces in nature.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Syracuse University Understanding Time and Space
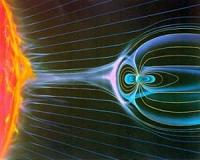 The Importance Of Being Magnetized
The Importance Of Being MagnetizedMoffett Field CA (SPX) Mar 23, 2011 Our nearest planetary neighbors, Mars and Venus, have no oceans or lakes or rivers. Some researchers have speculated that they were blown dry by the solar wind, and that our Earth escaped this fate because its strong magnetic field deflects the wind. However, a debate has arisen over whether a magnetic field is any kind of shield at all. The controversy stems from recent observations that ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |