 |
Palo Alto, Calif. (UPI) Mar 29, 2011 U.S. researchers say they've developed a battery that can generate electricity from the difference in salinity between fresh water and seawater. Anywhere fresh water enters the sea, such as river mouths or estuaries, could be potential sites for a power plant using such batteries, Yi Cui, Stanford University associate professor of materials science and engineering, said. Cui's team says if all the world's rivers were put to use, their batteries could supply about 2 terawatts of electricity annually, about 13 percent of the world's current energy consumption, a Stanford release said Tuesday. The battery consists of two electrodes, one positive and one negative - immersed in water containing electrically charged ions of sodium and chlorine, the components of ordinary table salt. The battery is filled with fresh water and a small electric current is applied to charge it. The fresh water is then drained and replaced with seawater, which because it is salty contains 60 to 100 times more ions than fresh water. This increases the electrical potential, or voltage, between the two electrodes, giving back far more electricity than the amount used to charge the battery. "If you charge at low voltage in fresh water, then discharge at high voltage in sea water, that means you gain energy," Cui said. "You get more energy than you put in."
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Powering The World in the 21st Century at Energy-Daily.com
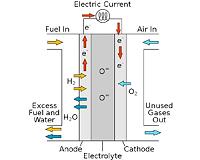 TU Delft Identifies Huge Potential Of Nanocrystals In Fuel Cells
TU Delft Identifies Huge Potential Of Nanocrystals In Fuel CellsDelft, Germany (SPX) Mar 29, 2011 The addition of extremely small crystals to solid electrolyte material has the potential to considerably raise the efficiency of fuel cells. Researchers at TU Delft were the first to document this accurately. Their second article on the subject in a very short time was published in the scientific journal, Advanced Functional Materials. The researchers at the Faculty of Applied Sciences at ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |